Have you ever wondered if viral infections, like hepatitis, could have a lasting impact on your liver? It’s a question that has significant implications for anyone who has experienced these infections or is interested in liver health. Understanding the relationship between viral infections and long-term liver damage can empower you to make informed decisions about your health and wellbeing. Let’s take a closer look at this fascinating topic to give you the insights you need.
Understanding Hepatitis and Other Viral Infections
Before exploring the potential for long-term damage, it helps to first understand what hepatitis and other viral infections are and how they affect your body. Viral infections occur when viruses invade your body’s cells, often causing disease in the process.
What is Hepatitis?
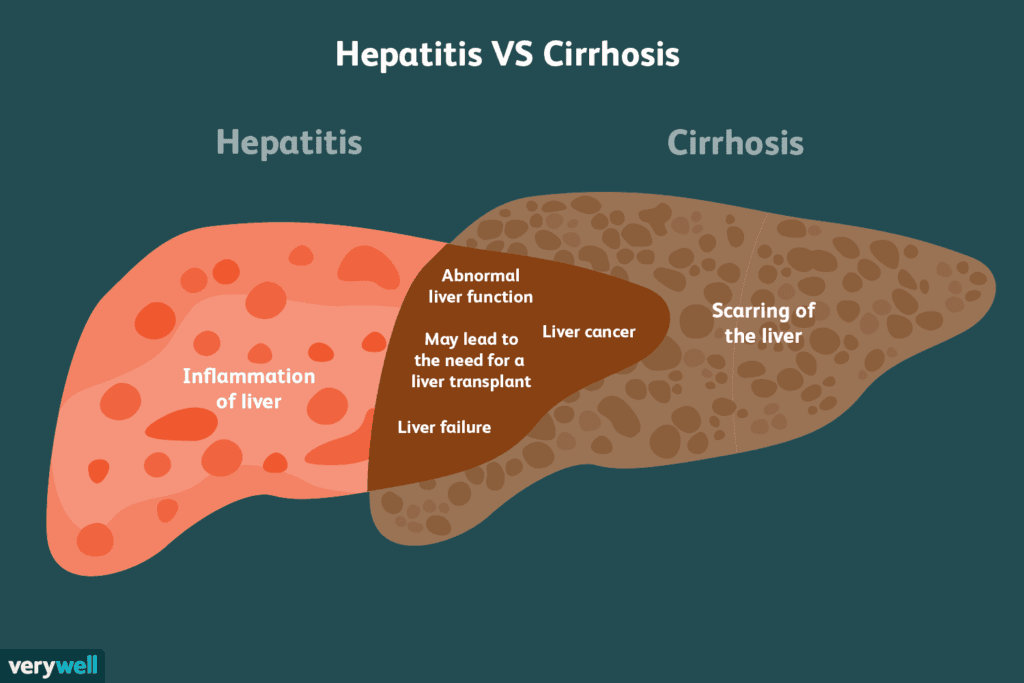
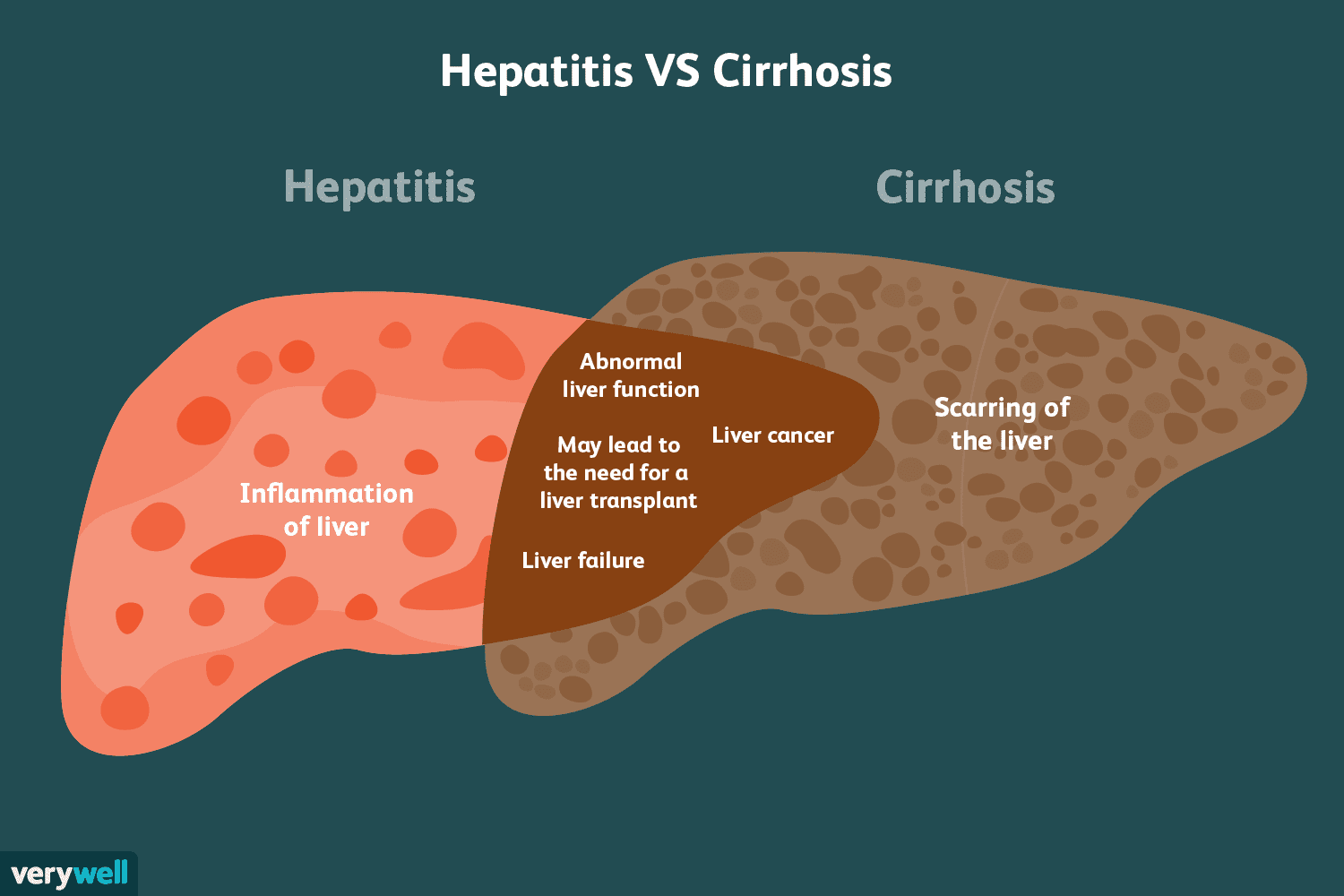
The term “hepatitis” refers to inflammation of the liver, which may be caused by viral infections, but can also result from other factors like alcohol, drugs, or autoimmune diseases. Of the various causes, viral infections are among the most common. The primary viruses involved in hepatitis are Hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E, each with distinct routines of transmission and effects on the liver.
Types of Viral Hepatitis
To better grasp how these viruses can affect your liver in the long run, it’s useful to explore the different types of viral hepatitis.
-
Hepatitis A: This is usually transmitted through the ingestion of contaminated food or water. It’s generally acute and self-limiting, meaning it does not typically lead to chronic liver disease.
-
Hepatitis B: Transmitted through contact with infected bodily fluids, this type can become chronic, leading to more severe health issues over time.
-
Hepatitis C: Often spread through blood-to-blood contact, this form is particularly notorious for becoming chronic and leading to long-term liver complications.
-
Hepatitis D: This requires the presence of Hepatitis B to infect a host and can exacerbate existing disease.
-
Hepatitis E: Typically spread through contaminated drinking water, this form is similar to Hepatitis A, causing acute but sometimes serious liver disease.
Other Viral Infections Impacting the Liver
Aside from hepatitis viruses, other viral infections can also lead to liver damage. For example, the Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus, often associated with other conditions, may sometimes cause liver inflammation (or hepatitis) as well.
How Viral Infections Cause Liver Damage
So, how exactly do these viral infections cause damage to your liver? The liver is an essential organ responsible for numerous metabolic and detoxifying processes. When it’s inflamed or otherwise compromised, these functions can be disrupted.
Mechanisms of Liver Damage
Viral infections can damage the liver through several mechanisms:
-
Direct Cytopathic Effects: Some viruses can directly harm liver cells (hepatocytes) by replicating within and ultimately destroying them.
-
Immune-Mediated Damage: Often, the damage isn’t directly from the virus itself but from your immune system’s response to the infection. The immune responses that normally protect you can also lead to collateral liver damage.
-
Chronic Infection: A persistent viral infection may lead to ongoing inflammation, which can gradually damage liver tissue over time.
Progression to Chronic Liver Disease
In some cases, particularly with Hepatitis B and C, the viral infections don’t resolve entirely, leading to chronic infection. Over time, chronic hepatitis can progress to more serious liver conditions, such as:
-
Fibrosis: Scarring of the liver, which happens as the body attempts to repair damage from chronic inflammation.
-
Cirrhosis: Advanced scarring that significantly impairs liver function and can potentially lead to liver failure.
-
Liver Cancer: The ongoing damage and regeneration cycles can increase the risk of developing liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma.

Symptoms and Diagnosis of Liver Damage
Detecting liver damage early can be crucial for managing your long-term health. Whether from a viral infection or another cause, liver damage can manifest in various ways.
Symptoms to Watch For
While some liver conditions are asymptomatic early on, there are signs you should be aware of:
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, caused by high levels of bilirubin.
- Fatigue and Weakness: General malaise and tiredness are common when the liver isn’t functionally optimally.
- Abdominal Pain and Swelling: Discomfort or bloating can be an indicator of liver issues.
- Dark Urine and Pale Stools: Changes in urine and stool color can indicate bilirubin metabolism issues.
Keep in mind that symptoms can vary based on the individual and the stage of liver damage.
Diagnostic Procedures
If you suspect liver damage, or if you’ve had a relevant viral infection, your healthcare provider might recommend several diagnostic tests:
-
Blood Tests: These assess liver enzyme levels, bilirubin, and identify antibodies to evaluate liver function and detect viral infections.
-
Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI can visualize liver structure and check for abnormalities.
-
Biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be needed to assess the extent of damage.

Management and Treatment of Viral Hepatitis and Liver Damage
Caring for a liver affected by viral infections is a multifaceted process, often involving both medical treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Medical Treatments
The approach to managing viral hepatitis and associated liver damage varies by the type of virus and the severity of the condition:
-
Antiviral Medications: Particularly for Hepatitis B and C, antiviral drugs can help control infection and reduce liver damage risk.
-
Vaccination: Vaccines are available for Hepatitis A and B, providing effective prevention.
-
Liver Transplant: In severe cases, such as liver failure or advanced cirrhosis, a transplant may be the only viable option.
Lifestyle Changes for Liver Health
Your liver health can also benefit significantly from lifestyle adjustments:
-
Diet: Eating a balanced diet low in saturated fat and high in fiber can aid in maintaining liver health.
-
Alcohol Avoidance: Alcohol can further stress the liver, so abstaining is often recommended.
-
Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reducing liver stress.
-
Avoiding Toxins: Limiting exposure to harmful substances can alleviate additional liver burdens.

Long-Term Outlook and Prevention
Understanding the potential consequences of viral infections on liver health underscores the importance of prevention and management.
Preventative Measures
Taking steps to prevent viral infections in the first place is crucial:
-
Safe Practices: Encourage safe sex and avoid sharing needles to reduce transmission risk.
-
Hygiene: Proper handwashing and food safety measures reduce Hepatitis A and E risk.
-
Vaccination: Getting vaccinated for Hepatitis A and B can provide robust protection.
Monitoring Your Liver Health
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help track your liver’s health, especially if you’ve had a prior infection. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve your long-term outlook.

Conclusion
Viral infections like hepatitis can indeed have a significant impact on your liver health. While some forms are more likely to lead to chronic conditions than others, understanding the risks, preventative measures, and treatments can help you manage and protect your liver effectively. Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and staying informed are some of the best ways to promote liver wellness and prevent long-term damage. By keeping your liver healthy, you can ensure it continues to perform its vital functions for years to come.