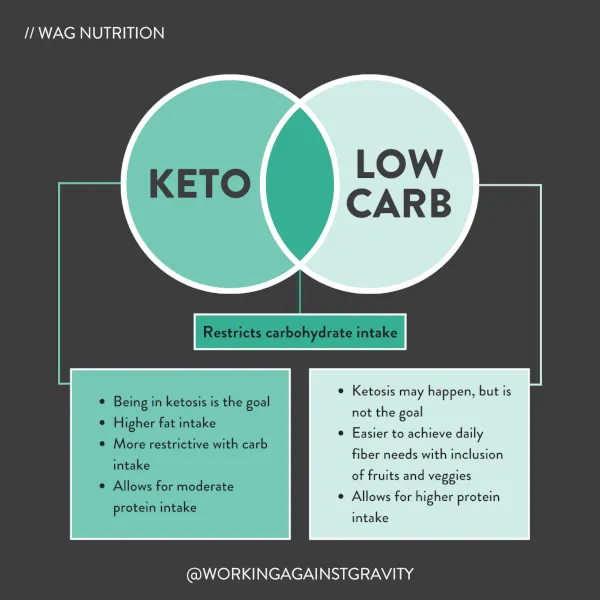
In recent years, the ketogenic (keto) diet has gained popularity as a way to lose weight and improve overall health. However, many people still confuse the keto diet with a low-carb diet, as both involve reducing carbohydrate intake. While they may seem similar on the surface, there are key differences between the two diets that can impact their effectiveness and potential health benefits.
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate diet that typically consists of 70-80% fat, 20-25% protein, and 5-10% carbs. The goal of the keto diet is to put the body into a state of ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of glucose. This can lead to rapid weight loss and improved energy levels, as well as potential benefits for conditions like epilepsy, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
On the other hand, a low-carb diet simply involves reducing carbohydrate intake to a certain extent, without necessarily increasing fat intake or aiming for ketosis. Low-carb diets can vary in their macronutrient ratios, but typically involve consuming less than 100-150 grams of carbs per day. This can still lead to weight loss and improved health, but may not have the same dramatic effects as a strict ketogenic diet.
One of the main differences between the keto and low-carb diets is the focus on fat intake. In the keto diet, fat is the primary source of energy, so followers must consume high amounts of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. In contrast, a low-carb diet may not require as much fat intake, as the body can still rely on glucose for energy.
Another key difference is the impact on ketosis. While both diets involve reducing carbohydrate intake, the keto diet specifically aims to put the body into ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel. This can lead to rapid weight loss and other health benefits, but may require more strict adherence to carbohydrate limits.
Overall, the ketogenic diet and low-carb diet both have their own benefits and drawbacks, and the best choice depends on individual goals and preferences. Some people may prefer the rapid weight loss and energy boost of the keto diet, while others may find a more moderate approach with a low-carb diet to be more sustainable in the long term.
In conclusion, while the ketogenic diet and low-carb diet both involve reducing carbohydrate intake, there are key differences in their macronutrient ratios, focus on fat intake, and impact on ketosis. Understanding these differences can help individuals choose the right approach for their health and weight loss goals. It’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet.