Hormone Regulation on the keto diet: What You Need to Know
The ketogenic diet, commonly known as the keto diet, has gained immense popularity in recent years for its ability to promote weight loss and improve overall health. One of the key factors that contribute to the success of the keto diet is its impact on hormone regulation in the body. Hormones play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including metabolism, energy production, and appetite control. By understanding how the keto diet affects hormone regulation, you can optimize your results and achieve your health and fitness goals more effectively.
In this article, we will delve into the mechanisms behind hormone regulation on the keto diet, how it impacts weight loss and overall health, and address common questions and concerns related to this topic.
How Hormones are Regulated on the keto diet
The keto diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to switch from using glucose as its primary source of energy to using ketones, which are derived from fat. This metabolic state, known as ketosis, has profound effects on hormone regulation in the body.
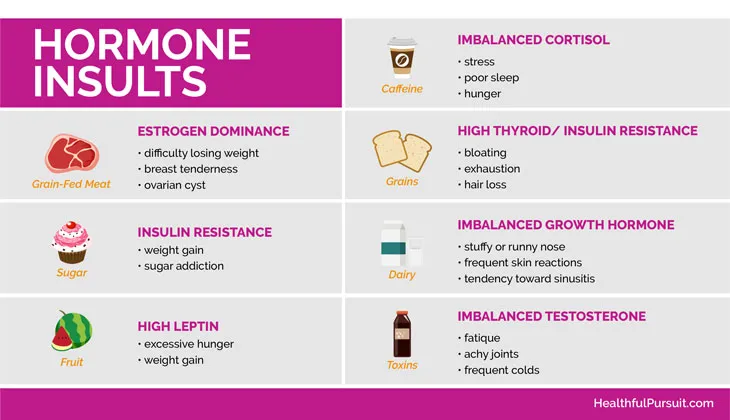
Insulin: Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas in response to elevated blood sugar levels. Its primary function is to facilitate the uptake of glucose into cells for energy production. When following a keto diet, carbohydrate intake is limited, resulting in lower blood sugar levels and reduced insulin secretion. This can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of insulin resistance, a condition linked to obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Glucagon: Glucagon is a hormone that works in opposition to insulin by promoting the breakdown of stored glycogen in the liver and the release of glucose into the bloodstream. On the keto diet, glucagon levels increase in response to low carbohydrate intake, leading to the breakdown of fat stores for energy production. This can help accelerate weight loss and improve metabolic health.
Leptin: Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that regulates appetite and energy expenditure. It signals to the brain when the body has enough energy stores and suppresses hunger. On the keto diet, the production of leptin may increase due to the high-fat content of the diet, leading to reduced appetite and improved satiety. This can help prevent overeating and promote weight loss.
Ghrelin: Ghrelin is a hormone produced in the stomach that stimulates appetite and promotes food intake. On the keto diet, ghrelin levels may decrease due to the reduced carbohydrate intake and increased fat consumption. This can help curb cravings and prevent excessive snacking, leading to better weight management.
Cortisol: Cortisol is a stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to physical or psychological stress. Chronic elevation of cortisol levels can lead to weight gain, inflammation, and metabolic dysfunction. The keto diet may help reduce cortisol levels by stabilizing blood sugar levels and promoting ketone production, which can have a calming effect on the body and improve stress resilience.
Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy production, and body temperature. Some studies suggest that the keto diet may have a mild suppressive effect on thyroid function, particularly in individuals with preexisting thyroid conditions. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of the keto diet on thyroid health.
Overall, the keto diet can have a profound impact on hormone regulation by promoting metabolic flexibility, improving insulin sensitivity, and optimizing appetite control. By balancing key hormones in the body, the keto diet can help enhance weight loss, increase energy levels, and improve overall health and well-being.
How Hormone Regulation Impacts Weight Loss on the keto diet
Hormone regulation plays a critical role in the success of weight loss on the keto diet. By optimizing key hormones involved in metabolism, appetite control, and energy expenditure, you can accelerate fat loss, preserve lean muscle mass, and achieve sustainable results.
Insulin: Insulin resistance is a common underlying factor in obesity and metabolic syndrome. By reducing carbohydrate intake and lowering insulin levels on the keto diet, you can improve insulin sensitivity and enhance fat burning. This can help break through weight loss plateaus and promote a leaner, more toned physique.
Leptin: Leptin resistance is another common issue in individuals struggling with weight loss. By increasing leptin production and sensitivity on the keto diet, you can better regulate hunger and cravings, leading to a more balanced caloric intake and improved weight management.
Ghrelin: Ghrelin is often referred to as the “hunger hormone” because it stimulates appetite and promotes food intake. By reducing ghrelin levels on the keto diet, you can curb cravings and prevent overeating, which is essential for maintaining a calorie deficit and losing weight effectively.
Cortisol: Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can hinder weight loss efforts by promoting fat storage, particularly in the abdominal area. By reducing cortisol levels through the stress-reducing effects of the keto diet, you can prevent excess weight gain and improve body composition.
Thyroid hormones: Thyroid dysfunction can slow down metabolism and lead to weight gain. While the keto diet may have a mild suppressive effect on thyroid function, it can still be an effective tool for weight loss when combined with proper nutrient intake and monitoring of thyroid health.
Overall, hormone regulation on the keto diet can have a significant impact on weight loss by promoting fat burning, reducing appetite, and improving metabolic health. By understanding how key hormones interact with the diet, you can tailor your approach to maximize results and achieve your desired body composition.
FAQs about Hormone Regulation on the keto diet
Q: Will the keto diet affect my menstrual cycle?
A: Some women may experience changes in their menstrual cycle when transitioning to the keto diet, particularly if they are initially under a high level of stress or have a history of hormonal imbalances. These changes are often temporary and may normalize as the body adapts to the new dietary pattern. If you notice any significant disruptions in your menstrual cycle, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying issues.
Q: Can the keto diet help with hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)?
A: The keto diet has shown promise in improving hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS, such as insulin resistance and excessive androgen production. By reducing carbohydrate intake and stabilizing blood sugar levels, the keto diet can help regulate hormone levels and alleviate symptoms of PCOS. However, individual responses to the diet may vary, and it’s important to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized approach to managing PCOS.
Q: Will the keto diet affect my thyroid function?
A: Some studies suggest that the keto diet may have a mild suppressive effect on thyroid hormones, particularly in individuals with preexisting thyroid conditions. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of the diet on thyroid health. If you have concerns about how the keto diet may impact your thyroid function, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider to monitor your thyroid levels and adjust your dietary approach accordingly.
Q: Can the keto diet help with adrenal fatigue?
A: Adrenal fatigue is a controversial term used to describe a cluster of symptoms related to chronic stress and adrenal dysfunction. While the keto diet may help reduce stress levels and stabilize cortisol production, it’s essential to address underlying causes of adrenal fatigue through lifestyle modifications, stress management techniques, and targeted supplementation. A holistic approach that considers individual needs and preferences is key to managing adrenal health effectively.
Q: Are there any potential side effects of hormone regulation on the keto diet?
A: While hormone regulation on the keto diet can have numerous benefits for weight loss and overall health, some individuals may experience temporary side effects such as changes in appetite, energy levels, or menstrual cycle. These effects are usually mild and tend to resolve as the body adapts to the new dietary pattern. It’s important to listen to your body, monitor your symptoms, and make adjustments as needed to ensure a positive and sustainable experience on the keto diet.
In conclusion, hormone regulation plays a crucial role in the success of the keto diet by optimizing metabolism, appetite control, and energy production. By understanding how key hormones interact with the diet, you can tailor your approach to maximize weight loss and improve overall health. By addressing common questions and concerns related to hormone regulation on the keto diet, you can feel confident in your decision to embark on this transformative dietary journey. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist before making any significant changes to your diet to ensure that it aligns with your individual needs and goals.