keto diet: A Promising Therapy for Managing Neurological Conditions
Introduction
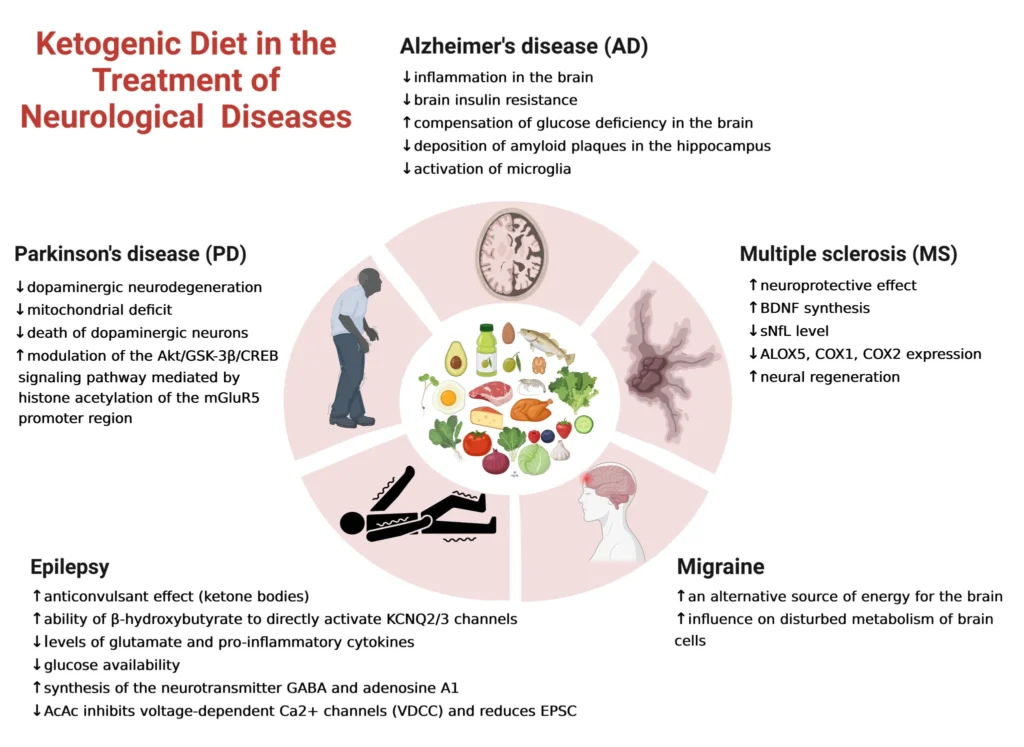
The ketogenic diet, often referred to as the keto diet, has gained popularity in recent years for its potential benefits in managing various health conditions, including neurological disorders. Originally developed in the 1920s as a treatment for epilepsy, the keto diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that forces the body to burn fat for fuel instead of glucose. In this article, we will explore the potential of the keto diet as a therapy for managing neurological conditions, including epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.
The Science Behind the keto diet
The keto diet works by inducing a state of ketosis, in which the body produces ketones as an alternative source of energy. Ketones are produced when the liver breaks down fats, and they can cross the blood-brain barrier to provide energy to the brain. This is thought to be beneficial for neurological conditions because the brain can use ketones more efficiently than glucose, especially in conditions where glucose metabolism is impaired.
Epilepsy
The keto diet has been used for almost a century as a treatment for epilepsy, particularly in children with drug-resistant epilepsy. Studies have shown that the keto diet can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in some patients. The exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed that ketones may have anti-seizure effects by stabilizing brain activity and reducing inflammation.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline and memory loss. Research suggests that the keto diet may have potential benefits for Alzheimer’s disease by improving brain function and reducing inflammation. Some studies have shown that the keto diet can improve cognitive function and memory in patients with mild cognitive impairment or early-stage Alzheimer’s disease.
Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects movement and coordination. Research on the keto diet in Parkinson’s disease is limited, but some studies suggest that the diet may have neuroprotective effects and improve motor symptoms. The keto diet may also help to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are thought to contribute to the progression of Parkinson’s disease.
Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, leading to inflammation and damage to the myelin sheath. Some research suggests that the keto diet may have potential benefits for multiple sclerosis by reducing inflammation and promoting neuroprotection. Studies in animal models of multiple sclerosis have shown that the keto diet can improve symptoms and slow disease progression.
FAQs
1. Is the keto diet safe for everyone?
The keto diet is generally considered safe for most people, but it may not be suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, liver disease, or pancreatitis, should consult with a healthcare provider before starting the keto diet. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also be cautious, as the keto diet may not provide enough nutrients for optimal fetal development.
2. How long does it take to see results on the keto diet?
The timeline for seeing results on the keto diet can vary depending on the individual and the specific neurological condition being treated. Some people may experience improvements in symptoms within a few weeks, while others may take several months to see noticeable changes. It is important to follow the keto diet consistently and work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor progress.
3. What are some common side effects of the keto diet?
Some common side effects of the keto diet include headache, fatigue, dizziness, constipation, and bad breath. These side effects are usually temporary and can be managed by staying hydrated, eating enough fiber, and ensuring adequate electrolyte intake. It is important to listen to your body and make adjustments to your diet as needed to minimize side effects.
4. Can I still take my medications while on the keto diet?
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen while on the keto diet. Some medications may need to be adjusted or monitored more closely when following a high-fat diet, as the keto diet can affect how medications are metabolized in the body. Healthcare providers can provide guidance on how to safely incorporate the keto diet with your current medications.
Conclusion
The keto diet shows promise as a therapy for managing neurological conditions, including epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. By inducing a state of ketosis, the keto diet can provide an alternative source of energy to the brain and may have neuroprotective effects. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of action and optimal protocols for different neurological conditions, the keto diet offers a potentially promising approach to managing these complex disorders. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider when considering the keto diet as a therapy for neurological conditions to ensure safe and effective treatment.